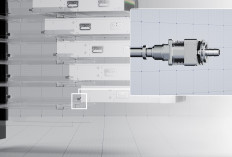
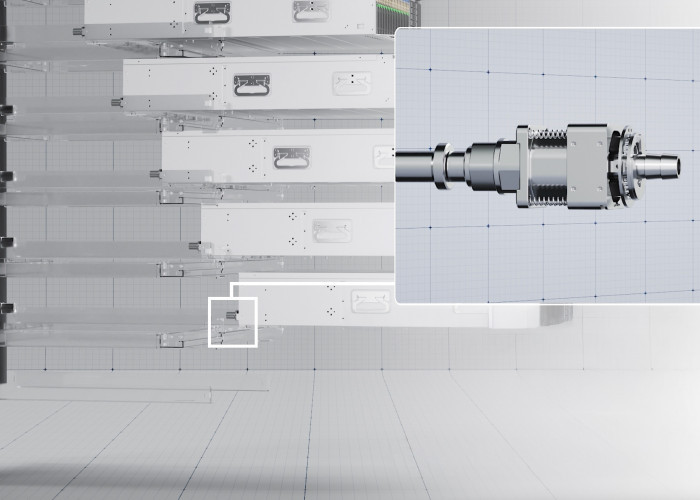
Southco’s Blind Mate Floating Mechanism Empowers Efficient Cooling in Data Centers
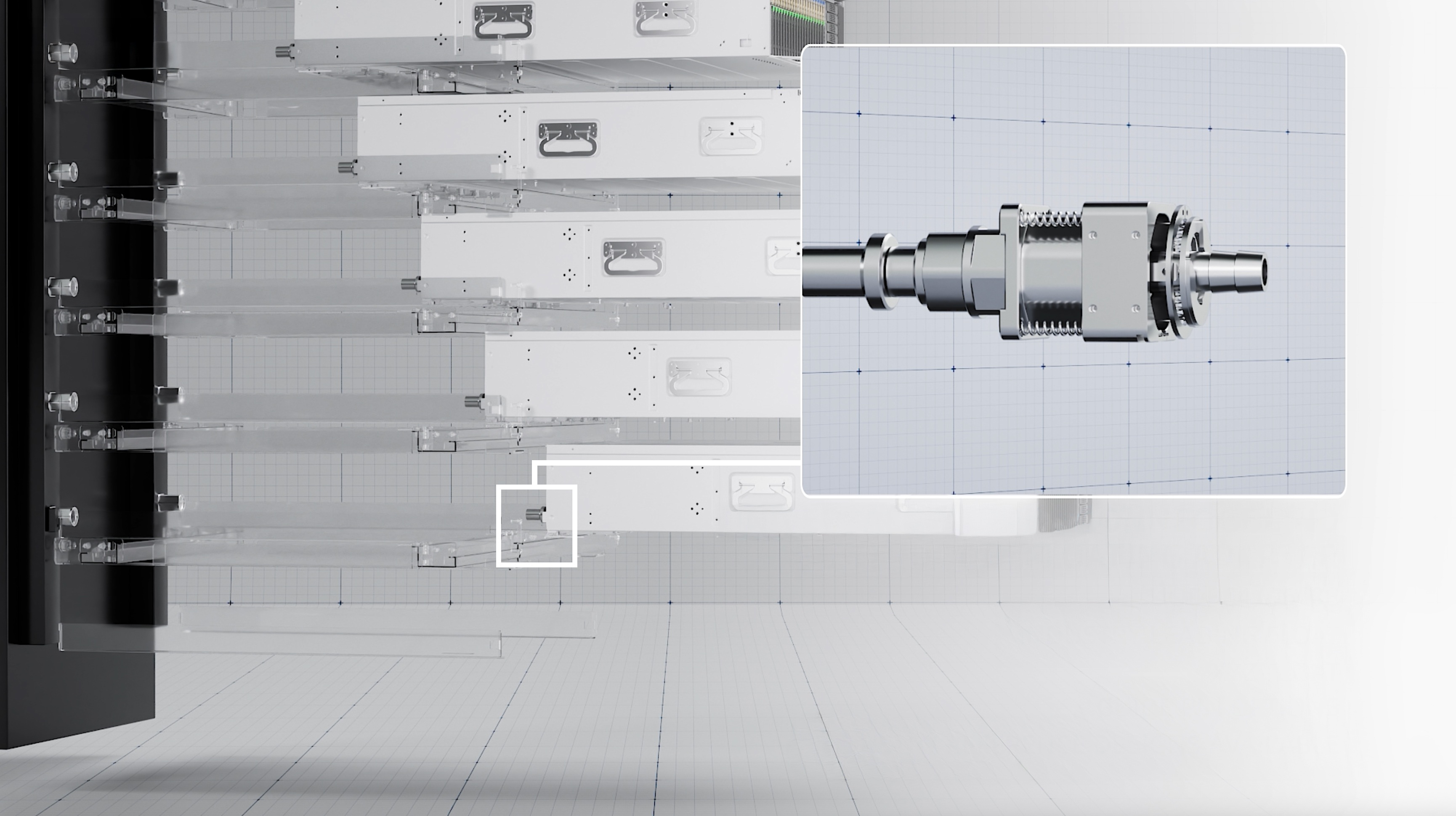
Southco’s Floating Mechanism--
HONG KONG SAR, Radarseluma.Disway.id - Global computing power is growing aggressively and pushing high-density chip power consumption. As this power density increases, traditional air cooling is reaching its physical limits, and once-fringe liquid cooling technology, boasting thermal efficiency hundreds of times greater than air cooling, is rapidly becoming core infrastructure.
BACA JUGA:Pajero Sport Model Baru: Desain Lebih Gagah dan Canggih Selalu Memikat Hati Para Penggemar Otomotif
BACA JUGA: Personalizing The Hong Kong Stay Experience With Dorsett Kai Tak’s ‘3 Wishes’ Package
Driven by global sustainability targets and the need for high-performance, energy-efficient infrastructures, new large data centers must achieve their targeted PUE values, accelerating the industry towards large-scale liquid cooling. However, reliability issues stemming from insufficient mechanical tolerances at the connection points of liquid cooling systems are becoming a critical bottleneck for energy efficiency upgrades and stable operation. Southco recognizes the severity of this challenge and is committed to providing breakthrough solutions.
Minor Deviations, Major Costs
During the large-scale deployment of liquid cooling technology, the reliability of connection interfaces is vital. According to key data from the Open Compute Project (OCP) "Rack-Mounted Manifold Requirements and Verification Guidelines," a mere 1mm increase in mechanical deviation at liquid cooling interfaces can significantly raise system flow resistance by 15%, leading to a 7% increase in pump energy consumption! This is no trivial amount; in a hyperscale data center with thousands of interfaces, it translates to millions of kilowatt-hours of additional energy consumption and substantial operational costs each year. More concerning is that traditional rigid connection solutions typically offer only ±0.5mm of static tolerance, which proves inadequate in complex real-world environments like these:
Accumulation of Multi-Dimensional Installation Deviations: In mixed deployment scenarios of widely used EIA-310-D standard racks and advanced ORV3 open architectures, rack installation tolerances can accumulate up to ±3.2mm, far exceeding the limits of traditional solutions.
Dynamic Vibration Impacts: In ISTA 3-E vibration tests simulating real transportation and operating environments, interface displacement often exceeds 2.8mm, posing significant risks of leaks or connection failures.
Material Thermal Expansion Effects: Under a typical temperature change of 55°C, copper alloy manifolds can expand approximately 1.2mm per meter, continuously challenging fixed interfaces.
These dynamic, multi-dimensional deviations underline the urgent need for an intelligent, reliable sealing connection solution to ensure the long-term, efficient, and safe operation of liquid cooling systems.
Sumber: media outreach newswire